Ear and deafness surgery stapes surgery
Ear discharge, hearing loss foreign body in ear, otosclerosis, grommet insertion for middle ear fluid ear malignancy.
You ear has three major parts: your outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. When damage to your outer or middle ear causes hearing loss, it is called conductive hearing loss. This type of hearing loss makes it hard to hear soft or low volume sounds. Conductive hearing loss may be either temporary or permanent, depending on the cause.
What are the symptoms of conductive hearing loss?
- sudden hearing loss
- pain in one or both of your ears
- a strange or unpleasant smell coming from your ear
- Generally, people with conductive hearing loss have difficulty hearing sounds at low volumes. This can lead to turning the sound up on headphones or on televisions and speakers.
Endoscopic Nasal Surgery (FESS) / Endoscopic sinus surgery
DNS, sinusitis, nasal allergy, rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal malignancy, sinus malignancy.
Endoscopic sinus surgery is a procedure used to remove blockages in the sinuses. These blockages may cause pain, drainage, recurring infections, impaired breathing or loss of smell.
Sinus surgery is used to relieve symptoms associated with:
- Sinusitis and nasal polyps
- Nasal congestion
- Nasal obstruction
- Recurrent or chronic sinus infections
- Nasal tumors
Endoscopic DCR / orbital decompression / optic nerve decompression
Chronic dacrocystites, orbital swelling, orbital trauma, sinus pathology leading to orbital complication
Dacrocystorhinostomy (DCR) was historically performed by ophthalmologists for nasolacrimal obstruction using external techniques.
Their adaption involves the preservation, rather than sacrifice, of nasal mucosa and the fashioning of anterior and posterior flaps of the lacrimal sac to achieve marsupialisation. To achieve this, full exposure of the sac is required and, as the upper half of the lacrimal sac lies above the insertion of the middle turbinate, removal of the hard bone of the lacrimal crest of the maxilla in this area is necessary.
The procedure is usually performed under general anaesthetic. The steps involved include:
- Pre-injection of the agger mucosa, middle turbinate and uncinate.
- Raising mucosal flap
- Exposing the lacrimal sac
- Lacrimal sac intubation
- Sac incision and sac flap creation
- Stenting/marsupilisation

Endoscopic Microlaryngeal Surgery
Benign laryngeal pathology like vocal cord nodule, vocal cord polyp, vocal cord cyst. Malignant pathology of larynx.
Micro Laryngeal Surgery is a surgical technique used in the evaluation and removal of various lesions of the vocal folds, including cancer, cysts, papilloma, polyps, and Reinke’s edema. A surgeon looks through the operating microscope and/or endoscope along with microinstruments to remove disease pathologies of the Larynx.
Microlaryngeal surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to biopsy or remove abnormal growths, such as granulomas or benign cysts, in the larynx. It is usually performed to correct voice disorders or to diagnose or treat laryngeal cancer. The majority of microscopic voice surgery procedures, though performed on an outpatient basis, are performed under general anesthesia to minimize the danger of gagging or breathing problems.
Flexible and rigid bronchoscopy / oesophagoscopy
Foreign body in bronchus, respiratory infection, benign pathology of lung Foreign body in esophagus , esophageal benign and malignant lesion.
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that lets doctors look at your lungs and air passages. It's usually performed by a doctor who specializes in lung disorders (a pulmonologist). During bronchoscopy, a thin tube (bronchoscope) is passed through your nose or mouth, down your throat and into your lungs.
Bronchoscopy is most commonly performed using a flexible bronchoscope. However, in certain situations, such as if there's a lot of bleeding in your lungs or a large object is stuck in your airway, a rigid bronchoscope may be needed.
Common reasons for needing bronchoscopy are a persistent cough, infection or something unusual seen on a chest X-ray or other test. Bronchoscopy can also be used to obtain samples of mucus or tissue, to remove foreign bodies or other blockages from the airways or lungs, or to provide treatment for lung problems.


Flexible Esophagoscopy
A flexible esophagoscopy involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into your esophagus. Tiny electrical cables run through the endoscope tube to shine light into the esophagus through a bundle of fibers as well as send images back to a monitor.
An esophagoscopy may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It may also be done if you have one or more of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- vomiting
- trouble swallowing
- constant feeling of having a lump in your throat
- a long-term cough that won't go away
- long-term heartburn that hasn't gone away with changes to your diet or by taking antacids
Head & Neck Cancer surgery / Advanced skull base surgery
Pituitary surgery, CSF leak surgery, meningocele surgery.
Many cancers of the head and neck can be cured, especially if they are found early. Although eliminating the cancer is the primary goal of treatment, preserving the function of the nearby nerves, organs, and tissues is also very important. When planning treatment, doctors consider how treatment might affect a person’s quality of life, such as how a person feels, looks, talks, eats, and breathes.
Overall, the main treatment options are surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Surgery or radiation therapy by themselves or a combination of these treatments may be part of the treatment plan.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of head and neck cancer, possible side effects, and the patient’s preferences and overall health. Take time to learn about all of your treatment options and be sure to ask questions about things that are unclear. Talk with your doctor about the goals of each treatment and what you can expect while receiving the treatment.
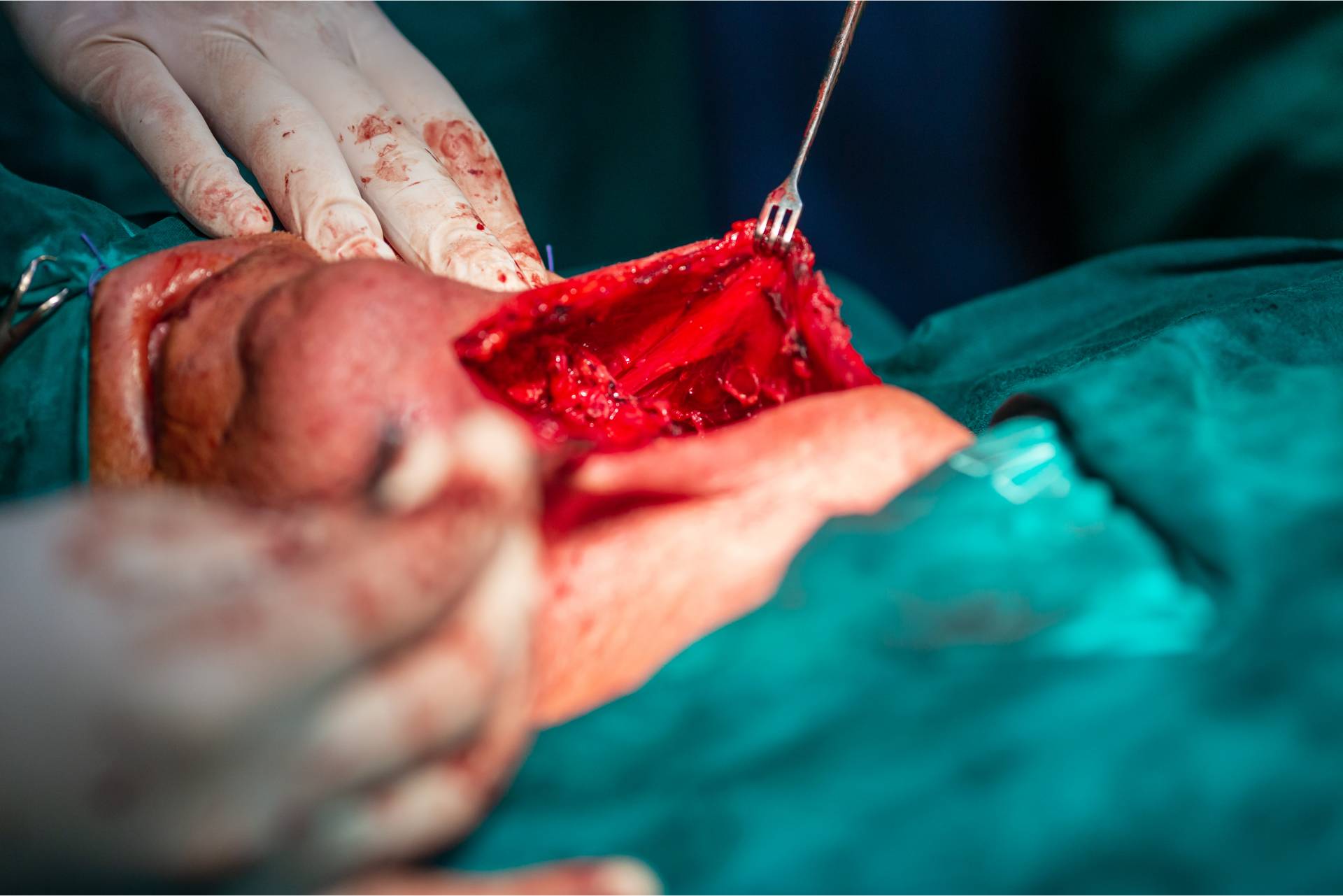
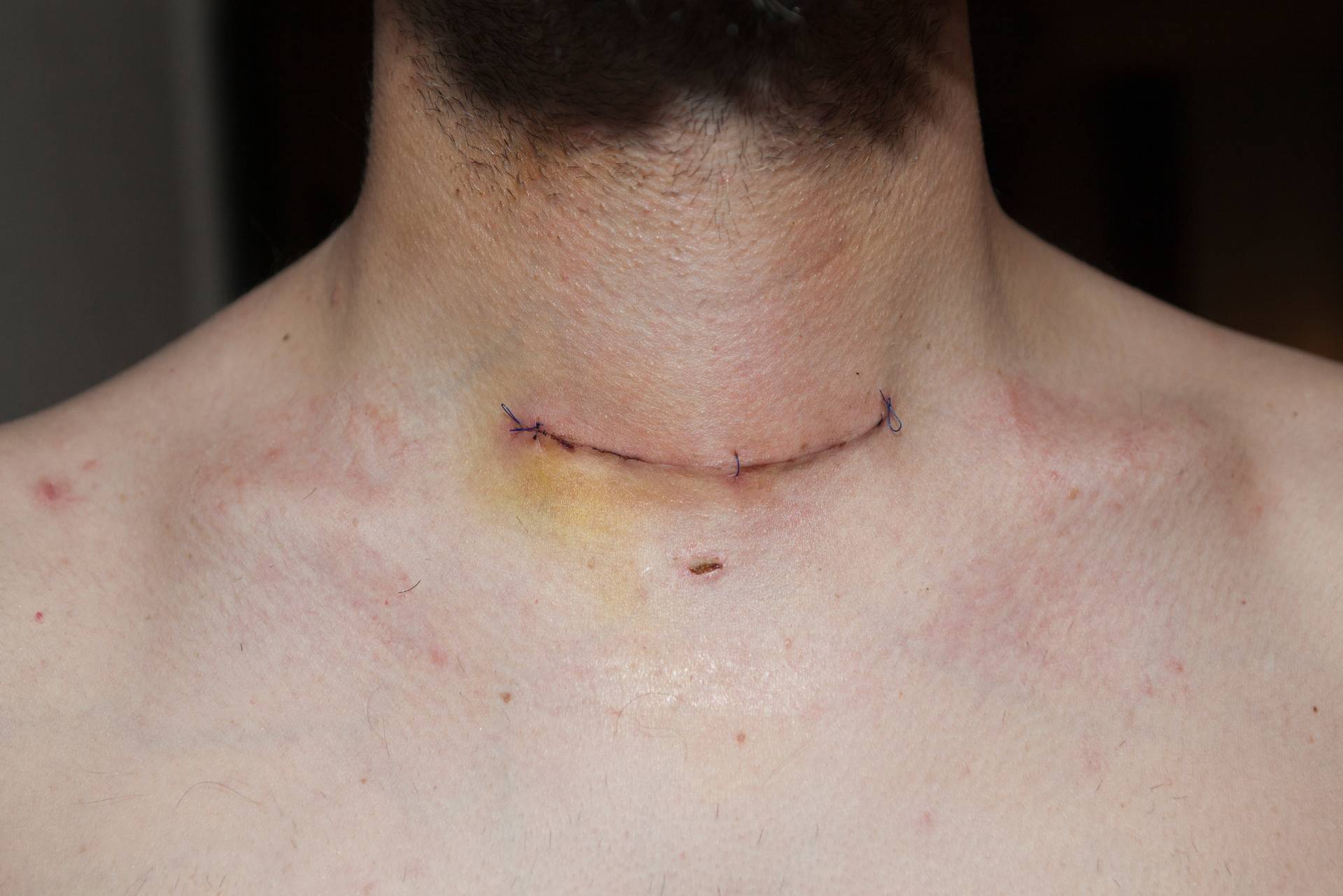
Thyroid Surgery
Oral cancer, thyroid cancer laryngeal cancer. Parotid cancer tongue cancer ear cancer nose cancer.
Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck. It produces hormones that control every aspect of your metabolism, from your heart rate to how quickly you burn calories.
Thyroidectomy is used to treat thyroid disorders, such as cancer, noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid (goiter) and overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
How much of your thyroid gland is removed during thyroidectomy depends on the reason for surgery. If you need only part of your thyroid removed (partial thyroidectomy), your thyroid may work normally after surgery. If your entire thyroid is removed (total thyroidectomy), you need daily treatment with thyroid hormone to replace your thyroid's natural function.
Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea surgery.
Snoring, sleep disturbances, obesity, and tonsilar enlargement, palatal and pharyngeal surgery for OSA
Sleep apnea is a type of sleep disruption that can have serious health consequences. It causes your breathing to periodically stop while you’re sleeping. This is related to the relaxation of the muscles in your throat. When you stop breathing, your body usually wakes up, causing you to lose out on quality sleep.
Over time, sleep apnea can increase your risk of developing high blood pressure, metabolic issues, and other health problems, so it’s important to treat it. If nonsurgical treatments don’t help, you may need surgery.
A sleep specialist can conduct additional evaluations to diagnose your condition, determine the severity of your condition and plan your treatment. The evaluation might involve staying at a sleep center overnight to monitor your breathing and other body functions as you sleep.


Rhinoplasty and cosmetic facial surgery
Fracture nasal bone facial trauma, deviated nasal bone.
Rhinoplasty, commonly referred to as a “nose job,” is surgery to change the shape of your nose by modifying the bone or cartilage. Rhinoplasty is one of the most common types of plastic surgery. People get rhinoplasty to repair their nose after an injury, to correct breathing problems or a birth defect, or because they’re unhappy with the appearance of their nose.
Possible changes that your surgeon can make to your nose through rhinoplasty include:
- a change in size
- a change in angle
- straightening of the bridge
- reshaping of the tip
- narrowing of the nostrils
Faciomaxillary Trauma Surgery
Also known as maxillofacial trauma, facial trauma refers to any injury affecting tissue or bones in the face or jaw. These types of injuries can be caused by things like car accidents, trips and falls, dog bites, burns or playing sports.
Common traumatic injuries to the face include:
- Ocular or orbital fracture
- Fractured cheekbone
- Fractured jaw
- Fractured forehead
- Fractured nose
- tumors
- Jaw tumors
- Fractures to the bone surrounding your teeth
- Dental injuries including broken or missing teeth
- Jaw dislocation and injuries
- Nasal cavity or sinus obstruction
- Palate injuries
- Soft tissue injuries, including cuts, scrapes, tissue loss and more

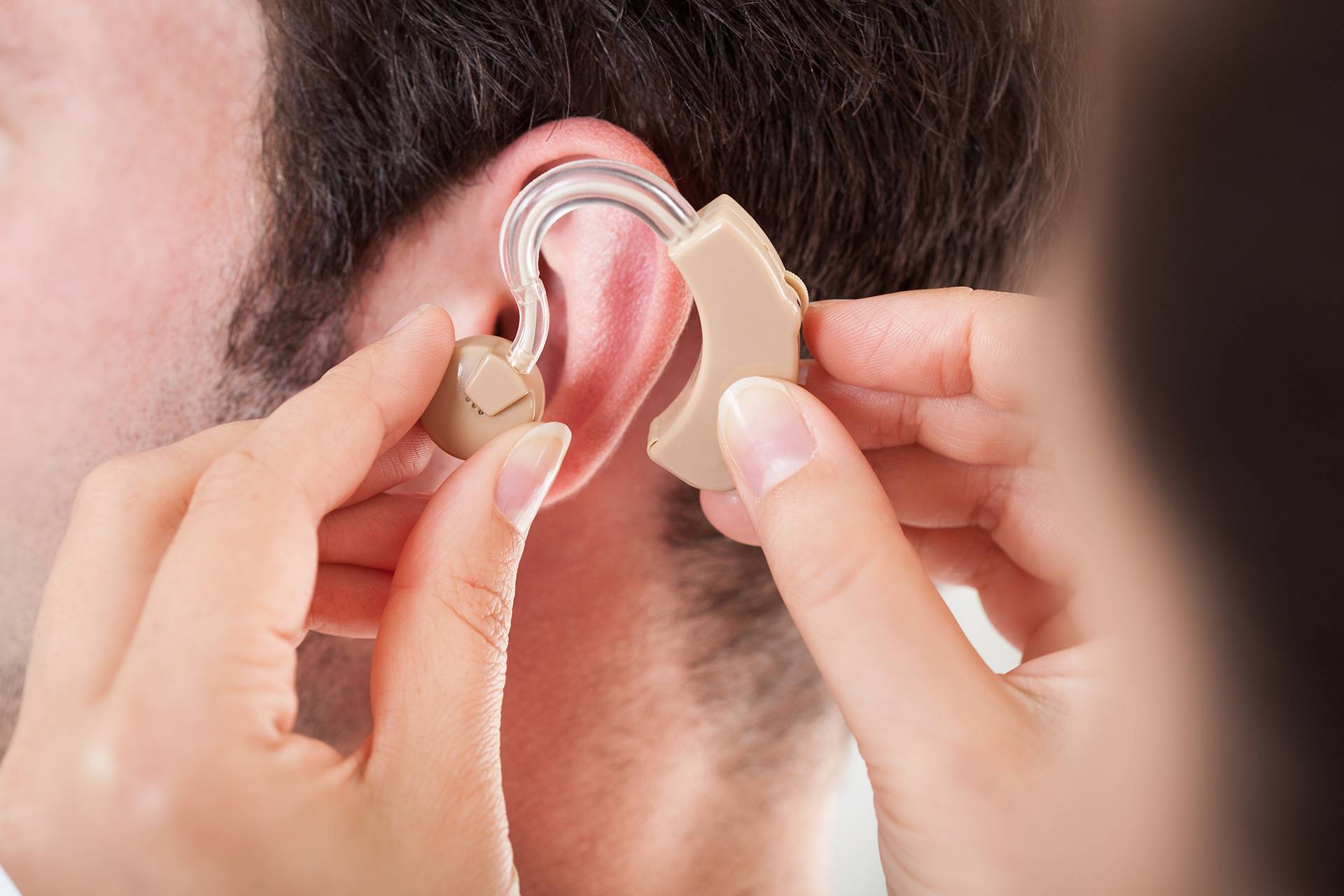
Hearing AID Facility
Hearing loss, presbycusis. A hearing aid is a small electronic device that you wear in or behind your ear. It makes some sounds louder so that a person with hearing loss can listen, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities.
A hearing aid has three basic parts: a microphone, amplifier, and speaker. The hearing aid receives sound through a microphone, which converts the sound waves to electrical signals and sends them to an amplifier. The amplifier increases the power of the signals and then sends them to the ear through a speaker.
Hearing aids are primarily useful in improving the hearing and speech comprehension of people who have hearing loss that results from damage to the small sensory cells in the inner ear, called hair cells. This type of hearing loss is called sensorineural hearing loss. The damage can occur as a result of disease, aging, or injury from noise or certain medicines.
Speech & Voice Therapy
Speech problem, change in voice, altered speech, stammering, slurred speech.
Whether you use your voice professionally or not, voice therapy can play an essential role in restoring and strengthening your voice.
The aim of voice therapy is to eliminate or improve problems with the creation of vocal sounds (phonation) in the larynx (voice box). After completing therapy, your voice should be stronger and sound like it did before. Voice therapy can also be used for prevention, to train your voice in order to avoid such problems altogether.
Voice therapy includes various individually tailored exercises that can be learned from a speech therapist, voice coach or respiratory therapist. In Germany, statutory health insurers typically cover the costs of voice therapy if it is necessary and has been prescribed by a family doctor or an ENT specialist.
Pediatric ENT care
Foreign body in ear nose removal, tongue tie surgery, cleft lip surgery. Tonsil adenoid surgery
- Allergies
- Hearing Problems
- Audiometry
- Sleep Apnea
- Problem Related Ear, Nose. Throat.
- VoiceBox Problem.
- swallowing problems

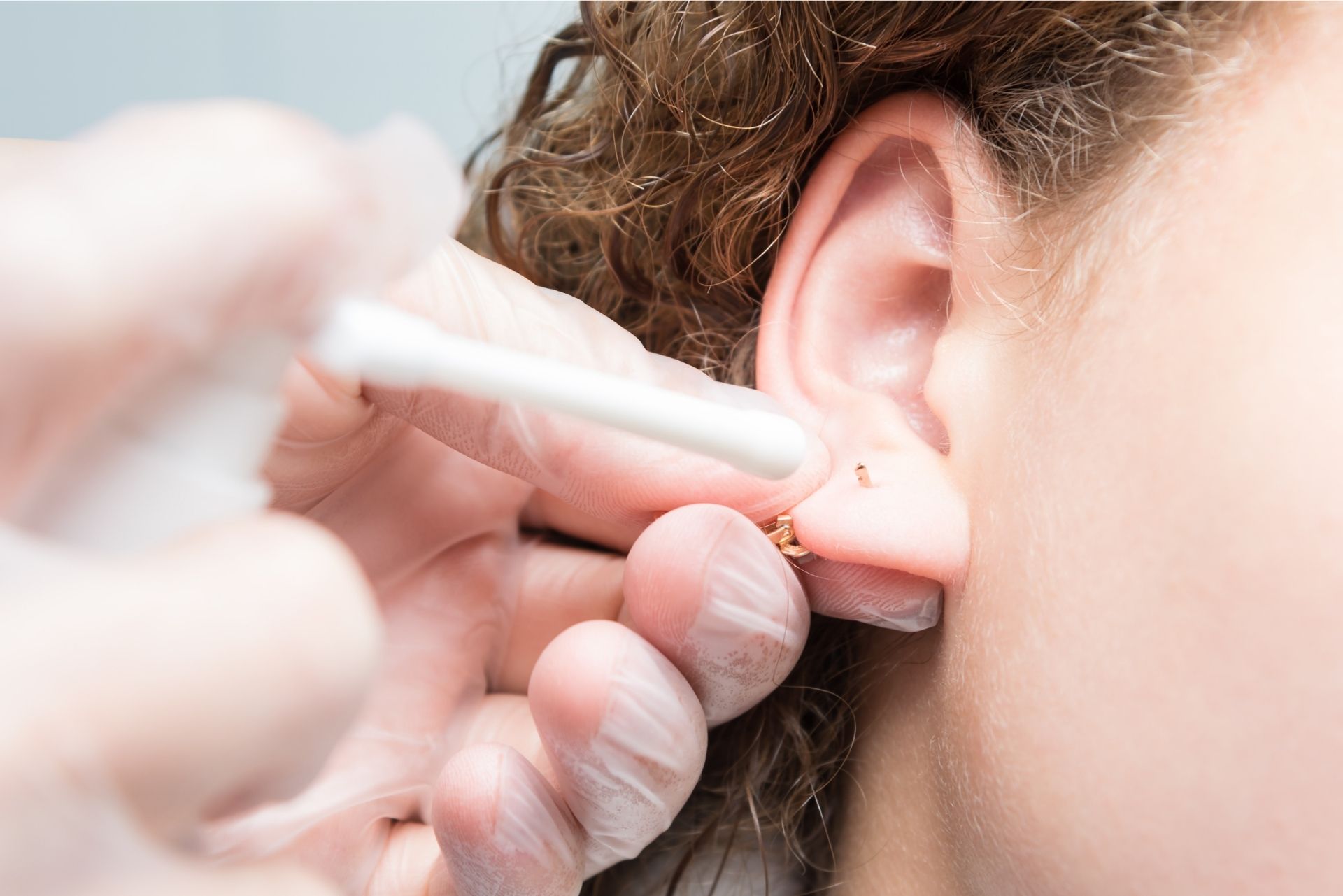
Ear piercing
For infants, young boy and girls.
When you get your ears pierced — whether at a tattoo parlor or a kiosk in the mall — you should receive instructions on how to prevent an infection. The vendor should also assure you that they only use sterile tools and hygienic practices.
But if protocol isn’t followed, or if you don’t carefully follow the post-piercing care instructions, infection can occur. You can usually treat a minor piercing infection of the earlobe fairly easily and without complications.